XABSL 笔记
introduction
A Bahavior FSM Engine developed by German Team @Martin Lötzsch
Config
- Compile XABSL agent
download the XabslEditor binary from [4]launchpad
Use XabslEditor.jar to edit .xabsl files
java -jar XabslEditor.jar
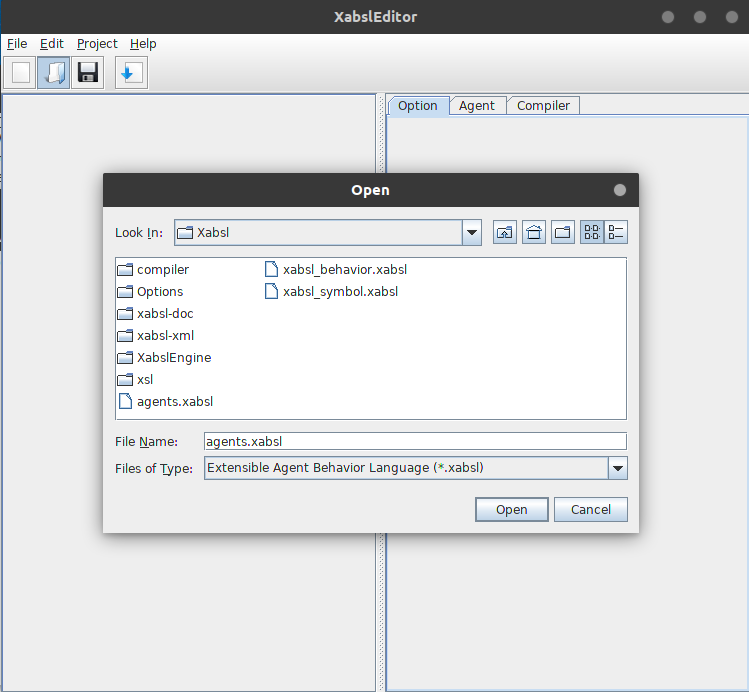
We have to modify three files at least in /Xabsl folder
agents.xabsl //define options files
xabsl_behavior.xabsl // define basic behavior class
xabsl_symbol.xabsl // define input/output symbols
agents.xabsl just like main.cpp, collect all .xabsl files.
include "xabsl_symbol.xabsl";
include "xabsl_behavior.xabsl";
include "Options/opt_head_gazebo.xabsl"; // entry to the game
agent Decision("Xabsl", opt_head_gazebo);
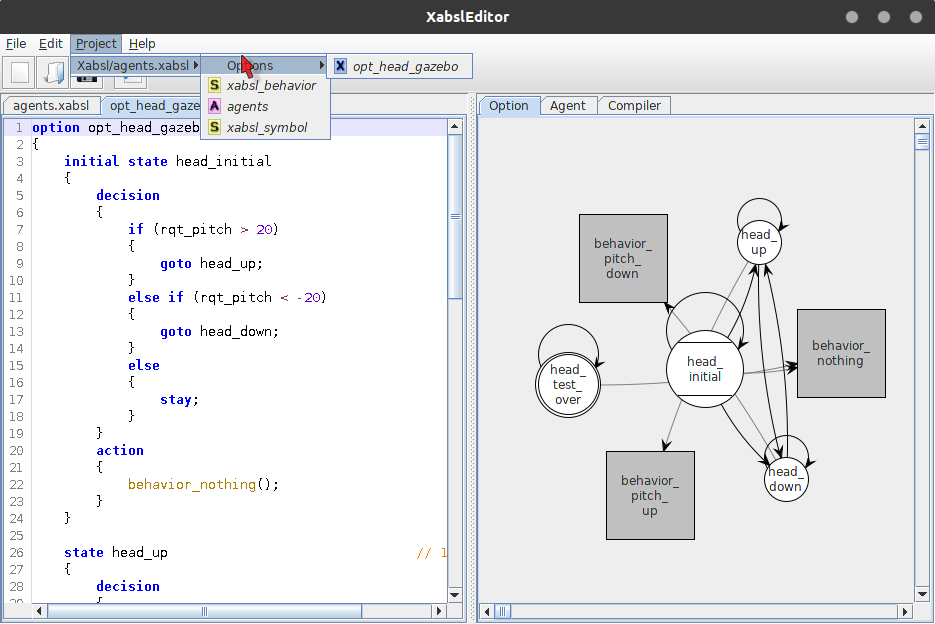
The symbols and behavior used in option.xabsl is declared in xabsl_symbol and xabsl_behavior
some time with error:
ruby warning: shebang line ending with \r may cause problems
em…DO NOTCompile the xabsl using ruby in options…
- register symbols and basic behavior in ROS node(C++ based)
File Structure:
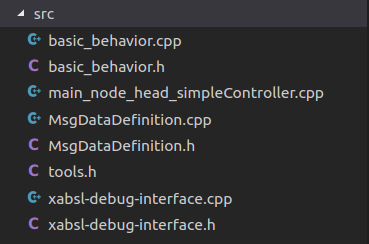
// File: main_node_head_simpleController.cpp
#include "MsgDataDefinition.h"
#include "tools.h"
#include "../Xabsl/XabslEngine/XabslEngine.h"
#include "basic_behavior.h"
#include "xabsl-debug-interface.h"
#include "std_msgs/Float64.h"
using namespace xabsl;
// using namespace decision;
// Global Data Structure.
MsgDataDefinition currentFrame;
MsgDataDefinition lastFrame;
MyErrorHandler errorHandler;
bool isInitializing = true;
std_msgs::String console_msg;
stringstream console_strstream;
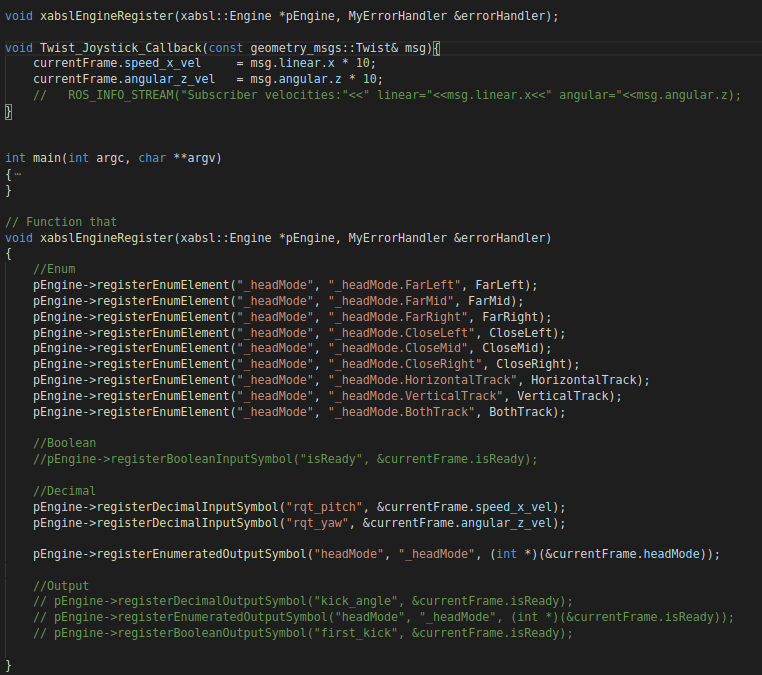
xabslEngineRegister register all symbol input&output with XABSL
basic_behavior.h/.cpp
class behavior_nothing : public BasicBehavior
{
public:
behavior_nothing(xabsl::ErrorHandler &errorHandler)
: xabsl::BasicBehavior("behavior_nothing", errorHandler)
{ }
virtual void registerParameters()
{
}
virtual void execute();
};
void behavior_nothing::execute()
{
//cout << "[BEHAVIOR]:nothing";
printf("[BEHAVIOR]:nothing");
}
负责将C++的basic behavior: 继承了BasicBehavior的子类和实现的虚函数excute()
MsgDataDefinition.h/.cpp
定义枚举类型以及所有决策需要的变量(和XABSL中变量一一对应)
main(): 读取.dat决策文件,注册所有basic behavior到xabsl
/*******************Xabsl Engine Read **.dat File*************************/
Engine *pEngine = new Engine(errorHandler, &getSystemTime);
MyFileInputSource inputSource("/$(package)/intermediate_code/opt_head_gazebo.dat"); xabslEngineRegister(pEngine, errorHandler);
/*******************Xabsl_behavior****************************************/
behavior_nothing _behavior_nothing(errorHandler);
behavior_pitch_up _behavior_pitch_up(errorHandler);
behavior_pitch_down _behavior_pitch_down(errorHandler);
pEngine->registerBasicBehavior(_behavior_nothing);
pEngine->registerBasicBehavior(_behavior_pitch_up);
pEngine->registerBasicBehavior(_behavior_pitch_down);
/******************Xabsle Creat Option Graph*****************************/
pEngine->createOptionGraph(inputSource);
//==========================Initial FSM==================================/
ROS_INFO("PAUSE!");
ros::Rate loop_rate(MAIN_NODE_RUNNING_RATE);
ROS_INFO("Initializing xabsl engine...\n");
debug_interface dbg(pEngine);
ROS_INFO("xabsl engine initialized, FSM starts to run...\n");
ros::ok() loop
while (ros::ok())
{
console_strstream.str("");
console_strstream << "\nround: " << ++roundCount << endl;
currentFrame.FlushData();
currentFrame.PrintReceivedData();
ROS_INFO("before execute");
pEngine->execute();
////////////debug
console_strstream << dbg.showDebugInfo().str()<< endl;
console_msg.data = console_strstream.str();
publish_decision_console.publish(console_msg);
cout << console_strstream.str() << endl;
ros::spinOnce();
loop_rate.sleep();
}
- Run!
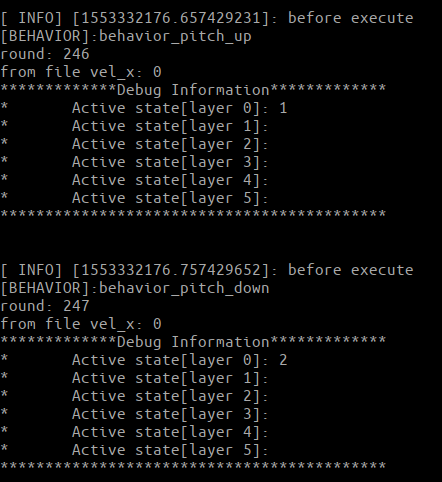
最简单的一个FSM...em…
Reference
[1] Martin Lötzsch, XABSL - A Behavior Engineering System for Autonomous Agents, Diploma Thesis.
[2] Martin Lötzsch, XABSL - A Pragmatic Approach to Behavior Engineering, IROS, 2006
[3] Thomas Röfer, B-Human, Team Report and Code Release 2011
[4] https://launchpad.net/xabsleditor/+download
[5] https://github.com/BerlinUnited/xabsleditor
[6] https://www.sim.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de